虚拟文件系统(VFS)是linux内核和存储设备之间封装的一层访问接口,通过这层接口,linux内核可以以统一的方式访问各种I/O设备。
虚拟文件系统本身是linux内核的一部分,是纯软件的东西,并不需要任何硬件的支持。它只存在于内存中,不存在于任何外存空间。VFS在系统启动时建立,在系统关闭时消亡。
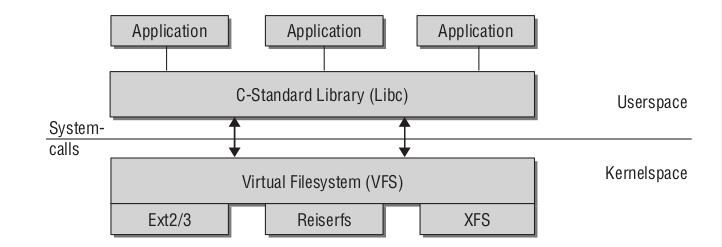
VFS 架构图
举个例子,将vfat格式的磁盘上的一个文件a.txt拷贝到ext3格式的磁盘 上,命名为b.txt。这包含两个过程,对a.txt进行读操作,对b.txt进行写操作。读写操作前,需要先打开文件,打开文件时,VFS会知道该文件对应的文件系统格式,以后操作该文件时,VFS会调用其对应的实际文件系统的操作方法。所以,VFS调用vfat的读文件方法将 a.txt的数据读入内存;将a.txt在内存中的数据映射到b.txt对应的内存空间后,VFS调用ext3的写文件方法将b.txt写入磁盘;从而实现了最终的跨文件系统的复制操作。
VFS通过一些数据结构及其方法向实际的文件系统如 ext2,vfat 提供接口机制。主要有以下4个数据结构:
- 超级块结构 (struct super_block {…} )
该结构保存了一个被安装在linux系统上的文件系统的信息。对于基于磁盘的文件系统,该结构一般和保存在磁盘上的”文件系统控制块”对应。也就是说如果是磁盘文件系统,该结构保存的磁盘文件系统的控制信息。/* * 超级块结构中定义的字段非常多, * 这里只介绍一些重要的属性 */ struct super_block { struct list_head s_list; /* 指向所有超级块的链表 */ const struct super_operations *s_op; /* 超级块方法 */ struct dentry *s_root; /* 目录挂载点 */ struct mutex s_lock; /* 超级块信号量 */ int s_count; /* 超级块引用计数 */ struct list_head s_inodes; /* inode链表 */ struct mtd_info *s_mtd; /* 存储磁盘信息 */ fmode_t s_mode; /* 安装权限 */ }; /* * 其中的 s_op 中定义了超级块的操作方法 * 这里只介绍一些相对重要的函数 */ struct super_operations { struct inode *(*alloc_inode)(struct super_block *sb); /* 创建和初始化一个索引节点对象 */ void (*destroy_inode)(struct inode *); /* 释放给定的索引节点 */ void (*dirty_inode) (struct inode *); /* VFS在索引节点被修改时会调用这个函数 */ int (*write_inode) (struct inode *, int); /* 将索引节点写入磁盘,wait表示写操作是否需要同步 */ void (*drop_inode) (struct inode *); /* 最后一个指向索引节点的引用被删除后,VFS会调用这个函数 */ void (*delete_inode) (struct inode *); /* 从磁盘上删除指定的索引节点 */ void (*put_super) (struct super_block *); /* 卸载文件系统时由VFS调用,用来释放超级块 */ void (*write_super) (struct super_block *); /* 用给定的超级块更新磁盘上的超级块 */ int (*sync_fs)(struct super_block *sb, int wait); /* 使文件系统中的数据与磁盘上的数据同步 */ int (*statfs) (struct dentry *, struct kstatfs *); /* VFS调用该函数获取文件系统状态 */ int (*remount_fs) (struct super_block *, int *, char *); /* 指定新的安装选项重新安装文件系统时,VFS会调用该函数 */ void (*clear_inode) (struct inode *); /* VFS调用该函数释放索引节点,并清空包含相关数据的所有页面 */ void (*umount_begin) (struct super_block *); /* VFS调用该函数中断安装操作 */ }; - 索引节点结构 ( struct inode {…} )
该结构中存储的是一个特定文件的一般信息,对于一个基于磁盘的文件系统,该结构对应磁盘上的”文件数据控制块”。每一个inode结构都对应一个inode节点号,这个节点号是唯一的,它也唯一标识一个文件系统中的文件。/* * 索引节点结构中定义的字段非常多, * 这里只介绍一些重要的属性 */ struct inode { struct hlist_node i_hash; /* 散列表,用于快速查找inode */ struct list_head i_list; /* 索引节点链表 */ struct list_head i_sb_list; /* 超级块链表超级块 */ struct list_head i_dentry; /* 目录项链表 */ unsigned long i_ino; /* 节点号 */ atomic_t i_count; /* 引用计数 */ unsigned int i_nlink; /* 硬链接数 */ uid_t i_uid; /* 使用者id */ gid_t i_gid; /* 使用组id */ struct timespec i_atime; /* 最后访问时间 */ struct timespec i_mtime; /* 最后修改时间 */ struct timespec i_ctime; /* 最后改变时间 */ const struct inode_operations *i_op; /* 索引节点操作函数 */ const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* 缺省的索引节点操作 */ struct super_block *i_sb; /* 相关的超级块 */ struct address_space *i_mapping; /* 相关的地址映射 */ struct address_space i_data; /* 设备地址映射 */ unsigned int i_flags; /* 文件系统标志 */ void *i_private; /* fs 私有指针 */ }; /* * 其中的 i_op 中定义了索引节点的操作方法 * 这里只介绍一些相对重要的函数 */ struct inode_operations { /* 为dentry对象创造一个新的索引节点 */ int (*create) (struct inode *,struct dentry *,int, struct nameidata *); /* 在特定文件夹中寻找索引节点,该索引节点要对应于dentry中给出的文件名 */ struct dentry * (*lookup) (struct inode *,struct dentry *, struct nameidata *); /* 创建硬链接 */ int (*link) (struct dentry *,struct inode *,struct dentry *); /* 从一个符号链接查找它指向的索引节点 */ void * (*follow_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *); /* 在 follow_link调用之后,该函数由VFS调用进行清除工作 */ void (*put_link) (struct dentry *, struct nameidata *, void *); /* 该函数由VFS调用,用于修改文件的大小 */ void (*truncate) (struct inode *); }; - 文件结构 ( struct file {…} )
该结构中存储的是一个打开的文件和打开这个文件的进程间的交互信息。该结构保存在kernel的内存区,在打开文件时被创建,关闭文件时被释放。/* * 文件对象结构中定义的字段非常多, * 这里只介绍一些重要的属性 */ struct file { union { struct list_head fu_list; /* 文件对象链表 */ struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead; /* 释放之后的RCU链表 */ } f_u; struct path f_path; /* 包含的目录项 */ const struct file_operations *f_op; /* 文件操作函数 */ atomic_long_t f_count; /* 文件对象引用计数 */ }; /* * 其中的 f_op 中定义了文件对象的操作方法 * 这里只介绍一些相对重要的函数 */ struct file_operations { /* 用于更新偏移量指针,由系统调用lleek()调用它 */ loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); /* 由系统调用read()调用它 */ ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); /* 由系统调用write()调用它 */ ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); /* 由系统调用 aio_read() 调用它 */ ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); /* 由系统调用 aio_write() 调用它 */ ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t); /* 将给定文件映射到指定的地址空间上,由系统调用 mmap 调用它 */ int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); /* 创建一个新的文件对象,并将它和相应的索引节点对象关联起来 */ int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); /* 当已打开文件的引用计数减少时,VFS调用该函数 */ int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id); }; - 目录项结构 ( struct dentry {…} )
该结构存储的是目录实体和对应的文件的关联信息。/* 目录项对象结构 */ struct dentry { atomic_t d_count; /* 使用计数 */ unsigned int d_flags; /* 目录项标识 */ spinlock_t d_lock; /* 单目录项锁 */ int d_mounted; /* 是否登录点的目录项 */ struct inode *d_inode; /* 相关联的索引节点 */ struct hlist_node d_hash; /* 散列表 */ struct dentry *d_parent; /* 父目录的目录项对象 */ struct qstr d_name; /* 目录项名称 */ struct list_head d_lru; /* 未使用的链表 */ /* * d_child and d_rcu can share memory */ union { struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */ struct rcu_head d_rcu; } d_u; struct list_head d_subdirs; /* 子目录链表 */ struct list_head d_alias; /* 索引节点别名链表 */ unsigned long d_time; /* 重置时间 */ const struct dentry_operations *d_op; /* 目录项操作相关函数 */ struct super_block *d_sb; /* 文件的超级块 */ void *d_fsdata; /* 文件系统特有数据 */ unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN_MIN]; /* 短文件名 */ }; /* 目录项相关操作函数 */ struct dentry_operations { /* 该函数判断目录项对象是否有效。VFS准备从dcache中使用一个目录项时会调用这个函数 */ int (*d_revalidate)(struct dentry *, struct nameidata *); /* 为目录项对象生成hash值 */ int (*d_hash) (struct dentry *, struct qstr *); /* 比较 qstr 类型的2个文件名 */ int (*d_compare) (struct dentry *, struct qstr *, struct qstr *); /* 当目录项对象的 d_count 为0时,VFS调用这个函数 */ int (*d_delete)(struct dentry *); /* 当目录项对象将要被释放时,VFS调用该函数 */ void (*d_release)(struct dentry *); /* 当目录项对象丢失其索引节点时(也就是磁盘索引节点被删除了),VFS会调用该函数 */ void (*d_iput)(struct dentry *, struct inode *); char *(*d_dname)(struct dentry *, char *, int); };目录项的目的就是提高文件查找,比较的效率,所以访问过的目录项都会缓存在slab中。可以通过如下命令查看:
[wangyubin@localhost kernel]$ sudo cat /proc/slabinfo | grep dentry dentry 212545 212625 192 21 1 : tunables 0 0 0 : slabdata 10125 10125 0

总结
VFS 即虚拟文件系统是Linux文件系统中的一个抽象软件层;因为它的支持,众多不同的实际文件系统才能在Linux中共存,跨文件系统操作才能实现。VFS 借助它四个主要的数据结构即超级块、索引节点、目录项和文件对象以及一些辅助的数据结构,向Linux中不管是普通的文件还是目录、设备、套接字等都提供同样的操作界面,如打开、读写、关闭等。只有当把控制权传给实际的文件系统时,实际的文件系统才会做出区分,对不同的文件类型执行不同的操作。由此可见, 正是有了VFS的存在,跨文件系统操作才能执行,Unix/Linux中的“一切皆是文件”的口号才能够得以实现。

很赞哦!